Uso: riscaldamento e raffreddamento
Use: heating and cooling
Abbinabile con:
Combined with:
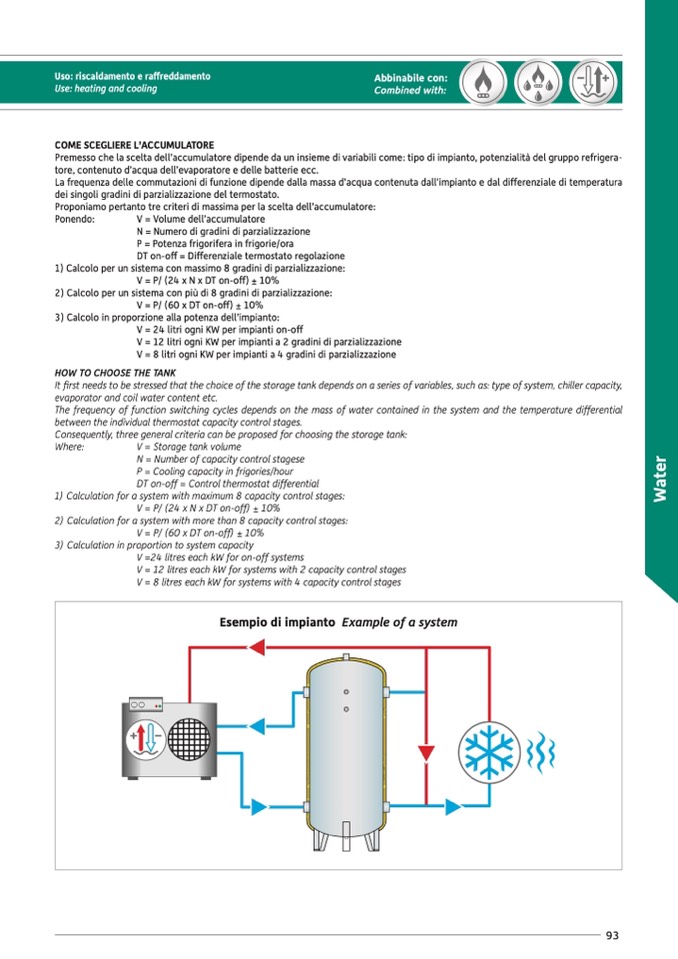
Esempio di impianto Example of a system
COME SCEGLIERE L’ACCUMULATORE
Premesso che la scelta dell’accumulatore dipende da un insieme di variabili come: tipo di impianto, potenzialità del gruppo refrigera-
tore, contenuto d’acqua dell’evaporatore e delle batterie ecc.
La frequenza delle commutazioni di funzione dipende dalla massa d’acqua contenuta dall’impianto e dal di
fferenziale di temperatura
dei singoli gradini di parzializzazione del termostato.
Proponiamo pertanto tre criteri di massima per la scelta dell’accumulatore:
Ponendo:
V = Volume dell’accumulatore
N = Numero di gradini di parzializzazione
P = Potenza frigorifera in frigorie/ora
DT on-off = Differenziale termostato regolazione
1) Calcolo per un sistema con massimo 8 gradini di parzializzazione:
V = P/ (24 x N x DT on-off) ± 10%
2) Calcolo per un sistema con più di 8 gradini di parzializzazione:
V = P/ (60 x DT on-off) ± 10%
3) Calcolo in proporzione alla potenza dell’impianto:
V = 24 litri ogni KW per impianti on-off
V = 12 litri ogni KW per impianti a 2 gradini di parzializzazione
V = 8 litri ogni KW per impianti a 4 gradini di parzializzazione
HOW TO CHOOSE THE TANK
It first needs to be stressed that the choice of the storage tank depends on a series of variables, such as: type of system, chiller capacity,
evaporator and coil water content etc.
The frequency of function switching cycles depends on the mass of water contained in the system and the temperature differential
between the individual thermostat capacity control stages.
Consequently, three general criteria can be proposed for choosing the storage tank:
Where:
V = Storage tank volume
N = Number of capacity control stagese
P = Cooling capacity in frigories/hour
DT on-off = Control thermostat differential
1) Calculation for a system with maximum 8 capacity control stages:
V = P/ (24 x N x DT on-off) ± 10%
2) Calculation for a system with more than 8 capacity control stages:
V = P/ (60 x DT on-off) ± 10%
3) Calculation in proportion to system capacity
V =24 litres each kW for on-off systems
V = 12 litres each kW for systems with 2 capacity control stages
V = 8 litres each kW for systems with 4 capacity control stages
93
W
a
t
e
r