Pompe di calore - Heat pumps
P
D
C
H
P
INTRODUZIONE
INTRODUCTION
La pompa di calore
è una macchina che sfrutta il ciclo
termodinamico del fluido refrigerante, trasferendo
il calore da una sorgente all’altra. In pratica, l’energia
termica presente nell’aria viene sfruttata per generare
capacità frigorifera o riscaldamento.
The heat pump is a device that exploits the
thermodynamic cycle of a refrigerant fluid transferring
heat from one source to another. In practice, it harnesses
the thermal energy present in the air to generate
refrigeration or heating capacity.
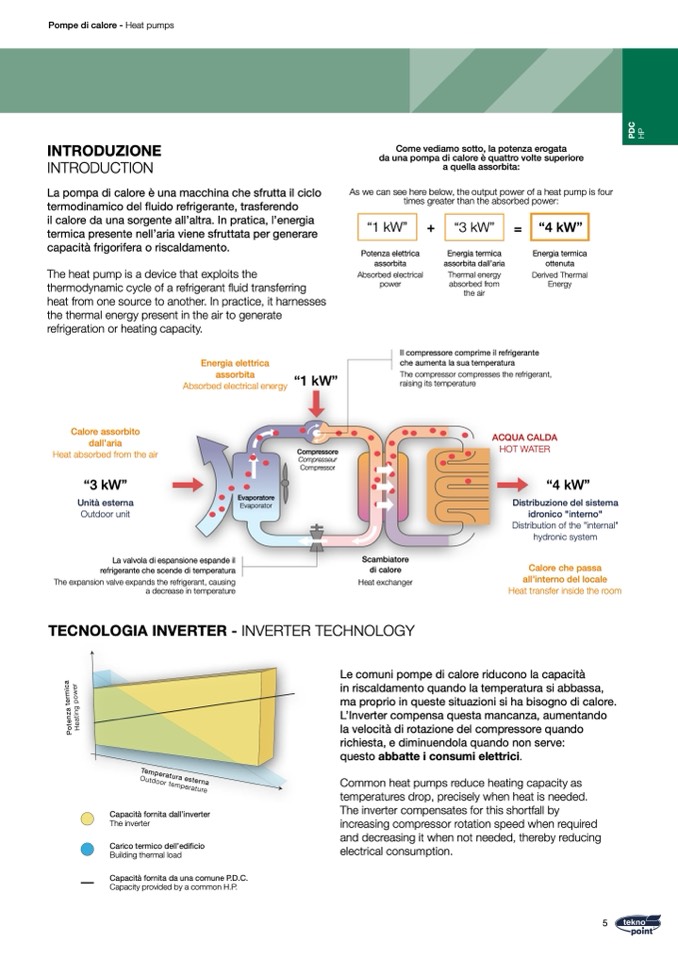
Come vediamo sotto, la potenza erogata
da una pompa di calore
è quattro volte superiore
a quella assorbita:
As we can see here below, the output power of a heat pump is four
times greater than the absorbed power:
Calore assorbito
dall’aria
Heat absorbed from the air
“3 kW”
Unit
à esterna
Outdoor unit
La valvola di espansione espande il
refrigerante che scende di temperatura
The expansion valve expands the refrigerant, causing
a decrease in temperature
Evaporatore
Evaporator
ACQUA CALDA
HOT WATER
“4 kW”
Distribuzione del sistema
idronico "interno"
Distribution of the "internal"
hydronic system
Calore che passa
all’interno del locale
Heat transfer inside the room
Energia elettrica
assorbita
Absorbed electrical energy
Il compressore comprime il refrigerante
che aumenta la sua temperatura
TECNOLOGIA INVERTER - INVERTER TECHNOLOGY
Capacità fornita dall’inverter
The inverter
Carico termico dell’edi
ficio
Building thermal load
Capacità fornita da una comune P.D.C.
Capacity provided by a common H.P.
Le comuni pompe di calore riducono la capacit
à
in riscaldamento quando la temperatura si abbassa,
ma proprio in queste situazioni si ha bisogno di calore.
L’Inverter compensa questa mancanza, aumentando
la velocit
à di rotazione del compressore quando
richiesta, e diminuendola quando non serve:
questo abbatte i consumi elettrici.
Common heat pumps reduce heating capacity as
temperatures drop, precisely when heat is needed.
The inverter compensates for this shortfall by
increasing compressor rotation speed when required
and decreasing it when not needed, thereby reducing
electrical consumption.
“1 kW”
Compressore
Compresseur
Compressor
The compressor compresses the refrigerant,
raising its temperature
Potenza elettrica
assorbita
Absorbed electrical
power
+
=
Energia termica
assorbita dall’aria
Thermal energy
absorbed from
the air
Energia termica
ottenuta
Derived Thermal
Energy
Scambiatore
di calore
Heat exchanger
5
“4 kW”
“1 kW”
“3 kW”
P
o
t
e
n
z
a
t
e
r
m
i
c
a
H
e
a
t
i
n
g
p
o
w
e
r
Tem
pe
ra
tu
ra
e
st
er
na
Ou
td
oo
r
tem
pe
ra
tu
re